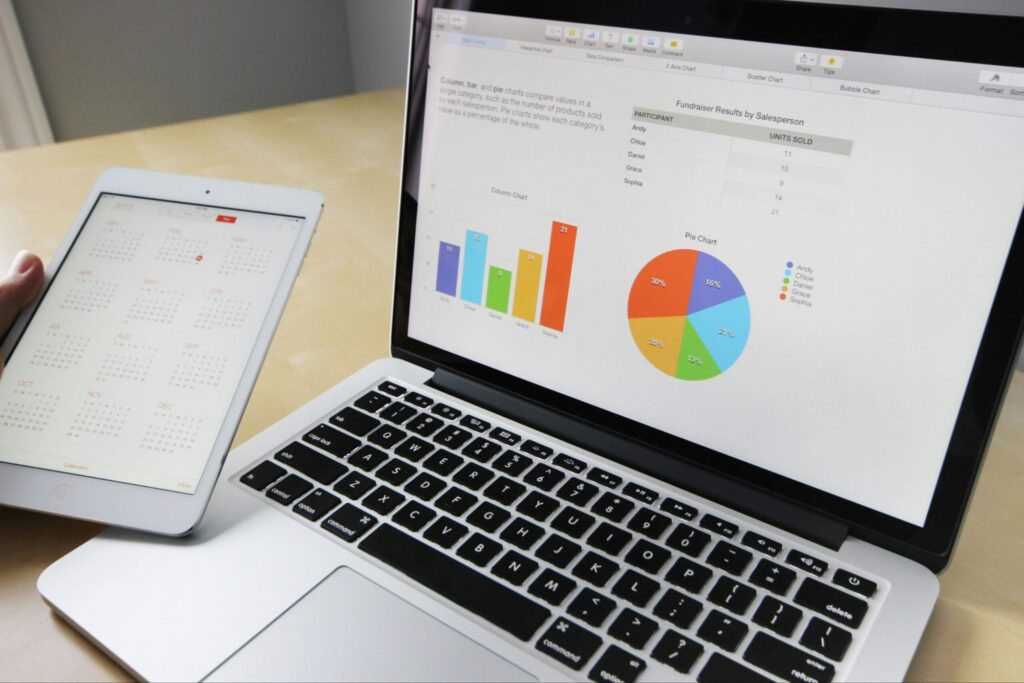
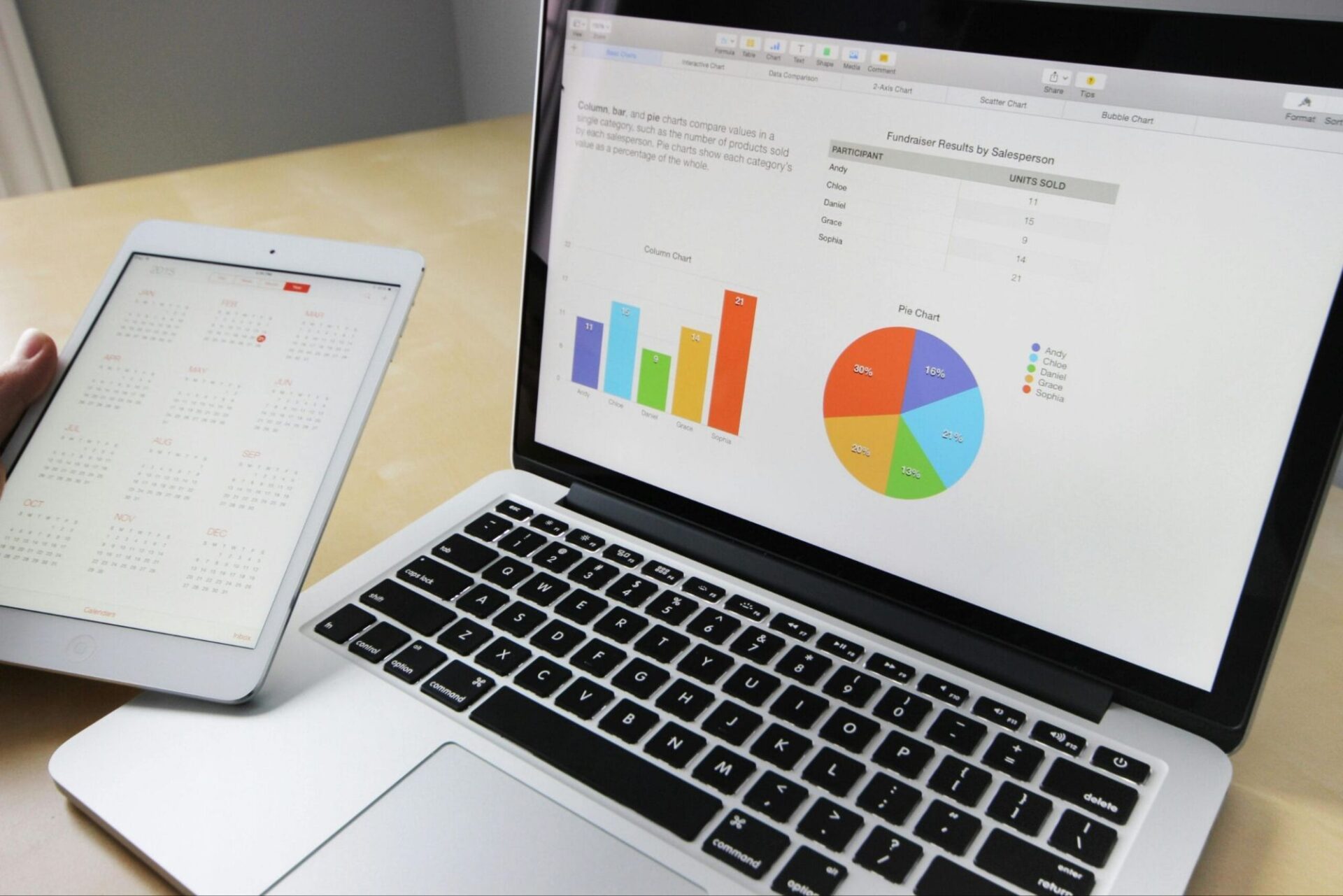
Indian Railways is ready to redefine long-distance train travel with its brand-new Vande Bharat Sleeper Trains — a perfect blend of speed, technology, and comfort. After the huge success of the Vande Bharat Express (chair-car version), this sleeper variant marks the next evolution in modern rail journeys across India.
What is the Bharat Sleeper Train?
The Vande Bharat Sleeper is a new version of the semi-high-speed Vande Bharat Express, designed especially for overnight journeys. Instead of only seats, this version will feature sleeping berths similar to Rajdhani trains — but with modern interiors, better comfort, and faster travel.
Indian Railways aims to gradually replace Rajdhani Express and other premium long-distance services with this high-tech train model.

Manufacturing and Production
The Vande Bharat Sleeper is being built by BEML (Bharat Earth Movers Limited) and Integral Coach Factory (ICF), Chennai.
- The first prototype was unveiled in September 2024.
- Trial runs have been successfully completed on the Mumbai–Ahmedabad route
- Indian Railways plans to roll out nine new sleeper trains by the end of 2025.
Why It’s Special
- Comfortable and luxurious overnight journeys
- Airline-like experience at a fraction of the price
- Faster travel between metros and major cities
- Completely ‘Make in India’ manufactured
- Eco-friendly design with reduced energy consumption
Expected Routes (Phase 1)
The first few routes likely to get Vande Bharat Sleeper services are:
- Delhi – Mumbai
- Howrah – Delhi
- Chennai – Bengaluru
- Mumbai – Ahmedabad
DIGI MERCH STORE PRINT ON DEMAND

Challenges Ahead
Minor design improvements are still underway (window curtains, berth spacing, etc.)
Tracks and signalling systems need further upgrades for high-speed operations.
Maintenance and cleanliness will be key to long-term success.
Conclusion
The Vande Bharat Sleeper Trains represent the dawn of a new era in Indian Railways — one that combines luxury, safety, and speed.
It’s not just another train — it’s a symbol of India’s modern engineering and self-reliant growth.
When these trains begin running by the end of 2025, passengers will experience an entirely new standard of overnight travel
sleepertrainroutes Facebookposts
VandeBharatExpress. LogosdogsGear
VandeBharatlaunch. WearableTech
Rajdhanireplacement. Businesscards
VandeBharatSleeperTrain. dailyprompt
Comment